Development of Blood-Forming Tissues
🔹 Embryogenesis
-
Hematopoietic stem cells arise around the 16 day of gestation in a portion of the ventral mesoderm referred to as the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region and the yolk sac.
Aorta-gonad-mesonephros region

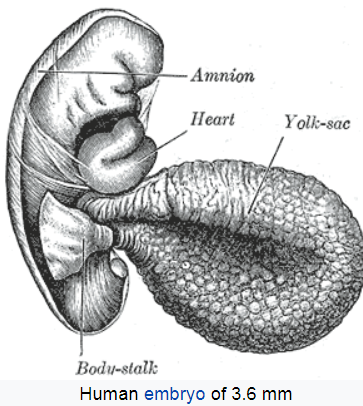
Yolk Sac
The hematopoietic progenitors generate the first (primitive) red cells and of multipotential definitive erythroid, megakaryocyte and myeloid progenitors that seed the fetal liver.
-
At this stage, mesoderm differentiates into hemangioblasts → blood islands → primitive blood cells and endothelium
🔹 Organogenesis
-
The full hematopoietic system as an organ system develops during organogenesis (week 3 onward).
-
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) emerge in the AGM region, then colonize the fetal liver, spleen, thymus, and bone marrow, which are forming organs.
This initial hematopoietic stem cell–independent program is ultimately replaced by a hematopoietic stem cell–derived program. Hematopoietic stem cells arise from intraembryonic arterial blood vessels and seed the fetal liver and the preterm marrow to generate definitive erythroid, megakaryocyte, myeloid and lymphoid progeny
-
These events establish the definitive hematopoietic organs (liver, bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes).
++++++++++++++++++++++
Hematopoietic stem cells derived from this region and the yolk sac migrate through the blood and take up residence in the liver.
The aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region is a crucial area in the developing embryo, specifically during vertebrate embryogenesis. It is named after its three main components:
1. **Aorta**: The major artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
2. **Gonads**: The organs that will develop into the testes or ovaries.
3. **Mesonephros**: A transient kidney structure that functions during early embryonic development.
The AGM region is especially important because it is a primary site for the emergence of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) during early development. HSCs are the precursor cells that will give rise to all the blood cells throughout an individual's life. These stem cells originate in the AGM region and later migrate to the fetal liver and, eventually, to the bone marrow, where they reside for the remainder of life.
T